SSA1 & SSA2
Both a first order solution (SSA1) and a second order solution (SSA2) are available. The code models the response of a bare isotropic rough soil simulating the normalized radar cross section (NRCS). The models provide the NRCS of the backscattering in both VV and HH polarizations. The following parameters must be given as input: radar frequency, incidence angle, soil moisture, surface roughness, correlation length (not necessary for IEMB and DB) and correlation function (not necessary for IEMB and DB). If a bistatic geometry is defined, the model provides 2-D maps NRCS a function of the zenith and azimuth scattering angles. An accurate characterization of the HV and/or VH NRCS is enabled by the use SSA2.
The code models the response of a bare isotropic rough soil simulating the normalized radar cross section (NRCS).
The figure below described the geometry of the observation of the target, which is bistatic in the most general case
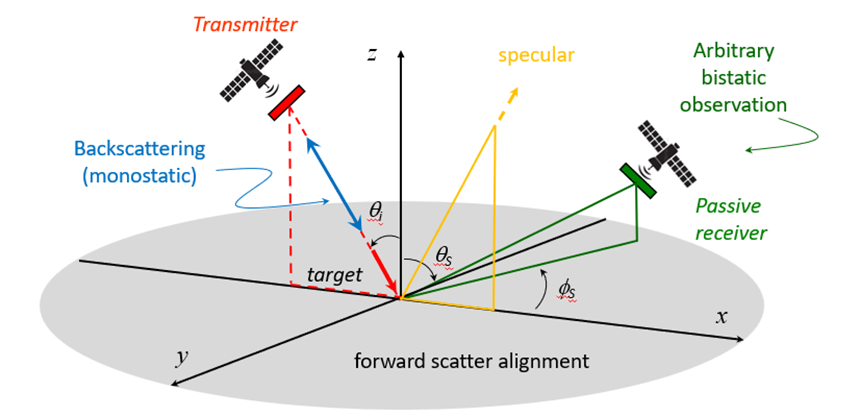
The model implements a numerical efficient solution of the integral describing the SSA solution of the scattering. The random nature of the surface is conventionally included by means of a statical gaussian representation.
The code can be used to generate arbitrary single values or bistatic maps of the NRCS describing co-polarized or cross-polarized scattering. Both the first and second order solution are provided. The second is computationally more demanding and is requested to achieve accurate solution of the cross polarized scattering within the incident plane and of the bistatic scattering. The two solutions can be compared, when needed, to assess the deviation of the first order with the respect to the second.
TBD
SSA: Small Slope Approximation
Voronovich A.G., “Small-slope approximation for electromagnetic wave scattering at a rough interface of two dielectric half-spaces,” Waves in Random Media, no. 4, pp. 337–367, 1994b.
D. Comite, and N. Pierdicca. "Monostatic and bistatic scattering modeling of the anisotropic rough soil," IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 57, no. 5 (2018): 2543-2556.
